Cloud Unveiled: A Majestic Journey through Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community Realms
Navigating the Cloudscape: A Deep Dive into Cloud Deployment Models for Unleashing Business Potential
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, the choice of deployment model plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization's digital strategy. Understanding the nuances of public, private, hybrid, and community clouds is crucial for businesses aiming to harness the full potential of cloud services. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve deep into each deployment model, unraveling their characteristics, advantages, and optimal use cases.
I. Public Cloud
Overview:
Public clouds are expansive digital landscapes provided by third-party service providers. Here, computing resources, applications, and storage are made available to the general public over the internet.
Characteristics:
Multi-Tenancy: Resources are shared among multiple users, optimizing costs through economies of scale.
Global Accessibility: Users can access resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go model ensures cost-effectiveness by charging only for consumed resources.
Advantages:
Scalability: Public clouds offer virtually limitless scalability to accommodate varying workloads.
Cost Savings: Organizations avoid upfront costs associated with maintaining physical infrastructure.
Use Cases:
Development and Testing: Ideal for cost-effective development and testing environments.
Web Applications: Hosting websites and applications with variable traffic demands.
Challenges:
Security Concerns: Shared resources raise concerns about data security and privacy.
Dependency on Service Provider: Reliability depends on the service provider's infrastructure and services.

II. Private Cloud
Overview:
Private clouds are dedicated infrastructures operated for a single organization, either on-premises or by a third-party provider.
Characteristics:
Single Tenancy: The entire cloud infrastructure is exclusive to a single organization.
Customization: Organizations can tailor the private cloud environment to meet specific requirements.
Data Security: Provides a higher level of control over data and compliance.
Advantages:
Enhanced Security: Organizations have full control over security measures, making it suitable for sensitive data.
Customization: Tailoring the infrastructure allows organizations to meet specific performance and compliance requirements.
Use Cases:
Sensitive Data Processing: Ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as finance and healthcare.
Mission-Critical Applications: Hosting applications with high performance and availability requirements.
Challenges:
Higher Initial Costs: Setting up a private cloud involves significant upfront costs.
Limited Scalability: May have limitations in scalability compared to public clouds.
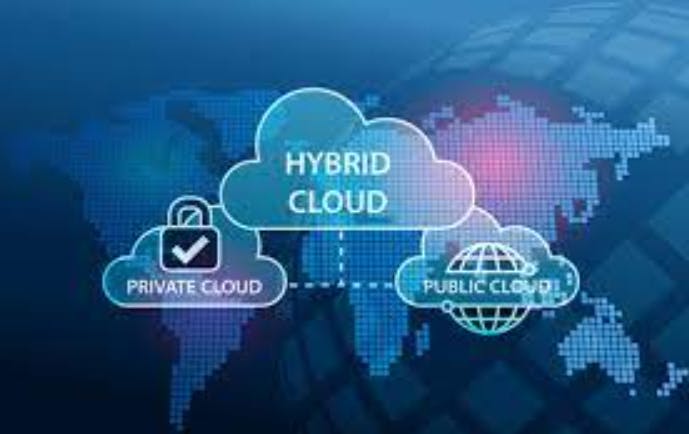
III. Hybrid Cloud
Overview:
Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared seamlessly between them.
Characteristics:
Interoperability: Data and applications can move seamlessly between public and private components.
Flexibility: Organizations can leverage the benefits of both public and private clouds based on specific needs.
Scalability: Provides a balance between the scalability of public clouds and the control of private clouds.
Advantages:
Flexibility and Agility: Organizations can dynamically allocate resources based on changing needs.
Optimized Costs: Allows organizations to use public resources for non-sensitive workloads and private resources for critical applications.
Use Cases:
Data Backup and Recovery: Storing critical data in a private cloud with backup in a public cloud for redundancy.
Bursting Workloads: Scaling resources dynamically by utilizing public cloud resources during peak demand.
Challenges:
Complexity: Managing and integrating resources across different environments can be complex.
Data Security and Compliance: Ensuring consistent security and compliance measures across both public and private components.

IV. Community Cloud
Overview:
Community clouds are shared infrastructures catering to the needs of a specific community or industry, with multiple organizations collaborating to use and manage the cloud.
Characteristics:
Collaboration: Community clouds foster collaboration among organizations within a specific industry or community.
Shared Resources: Resources are shared among organizations with similar requirements.
Cost Sharing: Participants share the costs of infrastructure, making it cost-effective.
Advantages:
Industry-Specific Solutions: Tailored to meet the specific needs and compliance requirements of a particular industry.
Resource Optimization: Sharing resources enables cost savings for organizations with similar computing needs.
Use Cases:
Government Agencies: Collaborating on shared infrastructure for public services.
Healthcare Networks: Sharing resources for medical research and data storage.
Challenges:
Community Consensus: Achieving consensus among community members on infrastructure and management can be challenging.
Data Security and Compliance: Ensuring that shared resources adhere to industry-specific security and compliance standards.

V. Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of a cloud deployment model is a strategic decision that profoundly influences an organization's digital journey. Whether embracing the scalability of public clouds, the control of private clouds, the flexibility of hybrid clouds, or the collaboration of community clouds, understanding the unique attributes of each model is essential.
By carefully evaluating factors such as data sensitivity, scalability requirements, cost considerations, and performance needs, businesses can make informed decisions aligned with their objectives. As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of emerging trends and considering real-world examples will empower organizations to optimize their cloud deployments for success in the digital age. The realm of cloud deployment models remains a dynamic and integral aspect of modern business operations, offering unparalleled opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and growth.
#NavigatingClouds ☁️ #CloudDeployment 💻 #DigitalTransformation 🚀 #TechInnovation 🌐 #BusinessStrategy 📈 #FutureTech 🔮 #CloudSolutions ☁️ #InnovateWithCloud 💡 #DigitalJourney 🌐 #StrategicTech 🛠️ #DataSecurity 🔒 #HybridCloud 🔄 #CommunityCloud 🌐 #CloudStrategy 🌩️ #Scalability 🚀 #CostEfficiency 💰 #TechTrends 🌐 #CloudEra ☁️ #CloudIntegration 🔗